What is a Stochastic Model
👤 Who
All users that are utilising Strategy Builder for modelling.
ℹ️ What is stochastic modelling and how is it used in iff?
Stochastic modelling predicts the likelihood of quantitative events by running a series of simulations. For iff, these events include clients' financial goals based on their current financial status. Each simulation represents a potential market condition, showcasing the volatility in investment returns over different periods.
The tool conducts hundreds of simulations using data gathered through the Fact-Finding process. These simulations are ranked by net asset value at life expectancy (of the longest-living client or partner). The sum of simulations resulting in positive net assets at life expectancy (after considering the clients' financial goals) determines the 'Asset Score' for the clients.
The median simulation is then displayed in the tool to show the potential impact of continuing with the current strategy or implementing one suggested by the adviser. The Cashflow Score is derived from the median simulation and represents the percentage of periods that have a net surplus cashflow.
ℹ️ What is the alternative?
A more commonly used approach is deterministic (or linear) projection. This method uses a static rate of return throughout the projected period and displays the results as a single line projection.
❗By default, all iff scenarios will display the median simulation from a stochastic model. A deterministic setting can be enabled on each scenario within strategy builder settings. Enabling the deterministic setting will remove the volatility associated with a stochastic model and apply the rate of returns specified within settings > portfolios > expected returns each month throughout the projection period. This option provides users with greater control and predictability in scenarios requiring fixed outcomes in view modelling charts/tables as well as your advice documents.
ℹ️ What is the difference?
Deterministic Modelling:
- Known inputs lead to known outputs.
- The same input will always produce the same output.
- Predictable and consistent behaviour.
- Generally expressed mathematically or computationally.
- Example: A recipe for baking a cake. Following the recipe will always produce the same cake.
Stochastic Modelling:
- Known inputs lead to a range of possible outputs.
- The same input can produce different outputs.
- Unpredictable and varied behaviour.
- Generally expressed as probability distributions.
- Example: predicting the stock market. Even though we know certain information about a company, the stock price can still fluctuate and have a range of possible values.
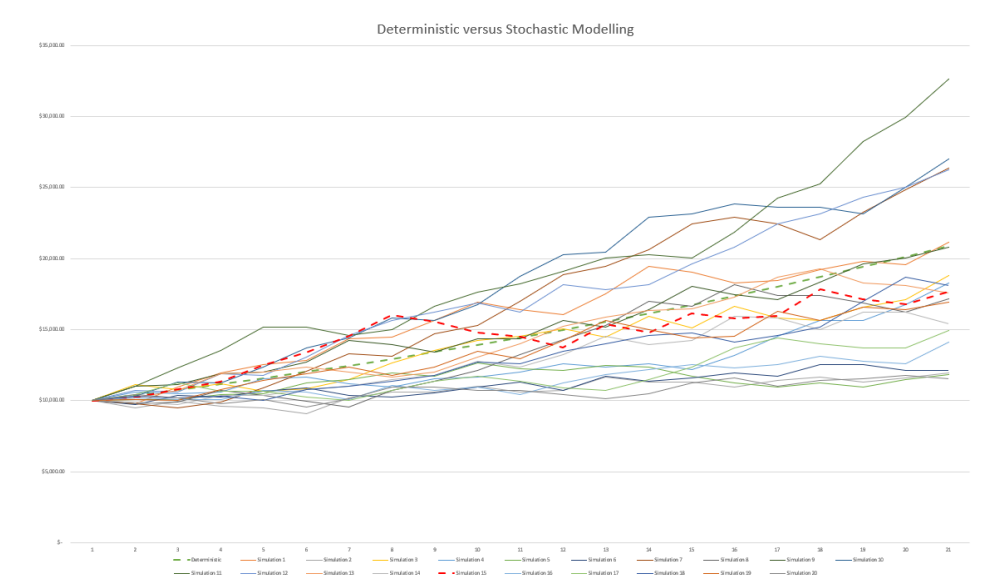
A graphical representation of this difference can be shown with a line chart. In a deterministic model, the line is straight, while in a stochastic model, it shows a band of possible values. For example, $10,000 invested over 20 years:
- The green dashed line represents the deterministic simulation with a 3.75% annual return.
- Other lines represent the 20-simulation stochastic model, where the rate varies between -5% and +12.5% per annum. The red dashed line is the median simulation of the stochastic model.